Mastering Programmable Logic Controller: Unlocking Automation Potential
 |
| Programmable Logic Controller |
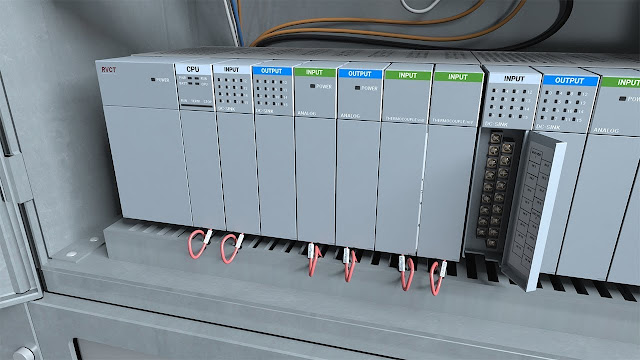
Programmable Logic Controller (PLCs) have revolutionized the industrial automation landscape, enabling efficient control and monitoring of complex processes. These versatile devices serve as the brains behind automation systems, providing the flexibility and reliability required for modern manufacturing environments. In this blog, we will delve into the world of PLCs, exploring their capabilities, applications, and benefits.
According to Coherent Market Insights the worldwide market
for Programmable
Logic Controller market had a worth of approximately $11.6 billion in 2021, and it is
anticipated to grow to around $18.3
billion by the year 2030, with a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.4% during the period
spanning from 2021 to 2030.
A Programmable Logic Controller is a specialized computerized
device designed to control and automate industrial processes. It is equipped with
input and output modules to interface with sensors, actuators, and other
devices. PLCs are programmed using ladder logic or other programming languages
to execute logic-based instructions and make real-time decisions.
PLCs find application in various industries such as
manufacturing, energy, automotive, and pharmaceuticals. They are used in
assembly lines, robotics, conveyor systems, and even power plants. PLCs excel
at tasks like process control, data acquisition, machine monitoring, and safety
systems. Their ability to handle multiple inputs and outputs, perform complex
calculations, and communicate with other systems makes them indispensable in
modern automation.
Flexibility: PLCs offer immense flexibility in modifying and
adapting automation processes. With the ability to change logic and reprogram
easily, PLCs allow for quick adjustments to accommodate production changes and
process optimizations.
Reliability: PLCs are known for their high reliability,
ensuring uninterrupted operation in critical environments. They are built to
withstand harsh conditions, electrical noise, and fluctuations, making them a
robust choice for industrial automation. PLC systems can be easily expanded or
modified to accommodate changes in production requirements. Additional I/O
modules, communication interfaces, or programming modifications can be
implemented without significant disruptions to the existing setup.
Diagnostics and Troubleshooting: PLCs provide extensive
diagnostics and logging capabilities, enabling efficient troubleshooting and
maintenance. They can monitor variables, detect faults, and generate alerts,
facilitating proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.


Comments
Post a Comment